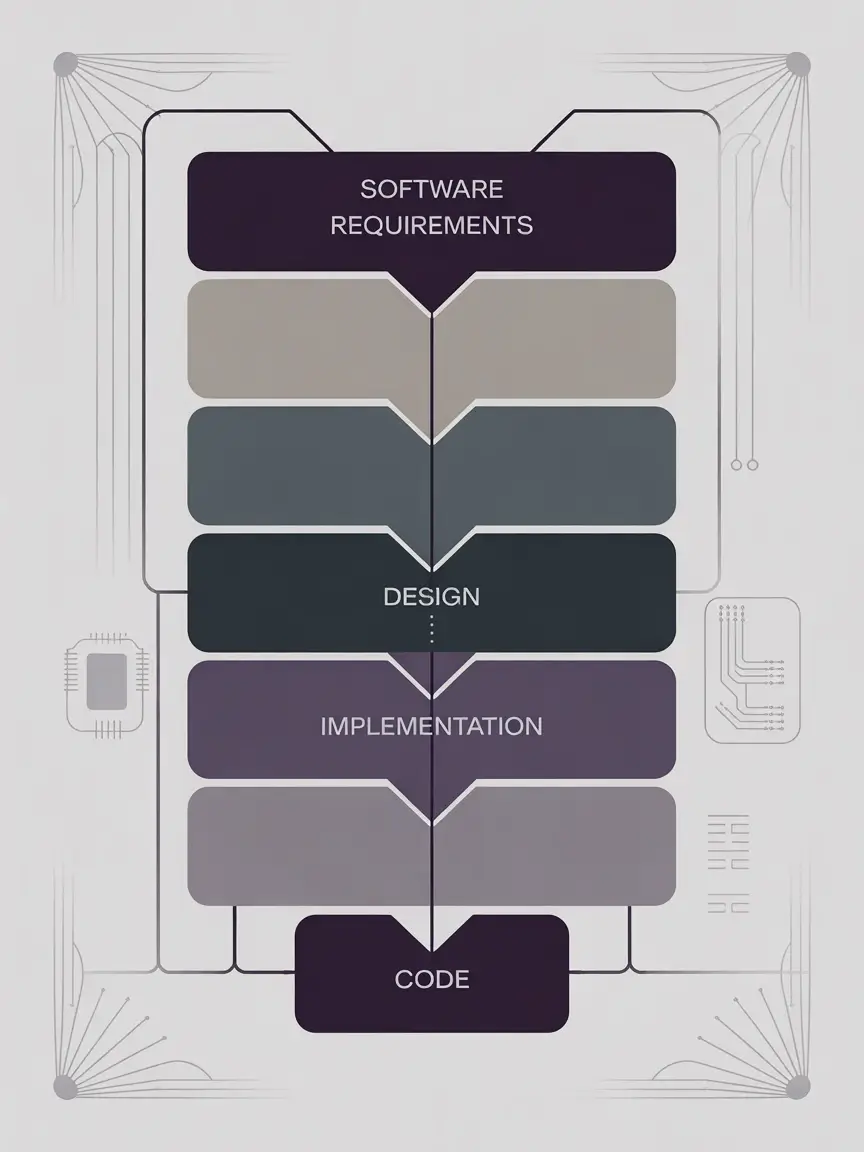
Intuitive Requirements Traceability
Managing your project's end-to-end traceability has never been this easier
DocSheets is intuitive and dramatically simplifies creating and synchronizing relationships. It is scalable to 1000s of items and relationships. Project team members can collaborate in real time without any update conflicts.